Tom Zahavy
These are my featured publications under three categories: General objectives for RL, meta gradients, and PhD work.
For a full list, see my Google scholar
General objectives for RL: We can describe the standard RL problem as a linear function, the inner product between the state-action occupancy and the reward vector. The occupancy is a distribution over the states and actions that an agent visits when following a policy and the reward defines a priority over these state-action pairs.
Sometimes, a good objective function is all we need; predicting the next word in a sentence turned out to be transformative. I've been interested in deriving more general objectives of behaviour: non linear, unsupervised, convex and non convex objectives that control the distribution that an agent visits. These include:
-
Maximum entropy exploration — visit all the states equally
-
Apprenticeship Learning — visit similar states to another policy
-
Diversity — visit states other policies do not
-
Constraints
-
And more
My main result is that we can reformulate these problems as convex-concave zero sum games, and derive a non stationary intrinsic reward for solving them. The reward turns out to be very simple and general; it is the gradient of the objective w.r.t to the state occupancy.
My papers below study the following questions:
-
In what sense are general utility RL problems different from RL problems?
-
Can we solve them with similar techniques?
-
Are there interesting objectives we can now easily solve using this approach?
-
In particular, I worked on Quality-Diversity objectives
Reward is enough for convex MDPs, NeurIPS 2021 (spotlight)
Tl;dr: we study non linear and unsupervised objectives that are defined over the state occupancy of an RL agent in an MDP. These include Apprenticeship Learning, diverse skill discovery, constrained MDPs and pure exploration. We show that maximizing the gradient of such an objective, as an intrinsic reward, solves the problem efficiently. We also propose a meta algorithm and show that many existing algorithms in the literature can be explained as instances of it.
Tom Zahavy, Brendan O'Donoghue, Guillaume Desjardins, Satinder Singh
Discovering Policies with DOMiNO: Diversity Optimization Maintaining Near Optimality
ICLR 2023
Tl;dr We propose intrinsic rewards for discovering quality-diverse policies and show that they adapt to changes in the environment.
Discovering a set of policies for the worst case reward, ICLR 2021 (spotlight)
Tl;dr We propose a method for discovering a set of policies that perform well w.r.t the worst case reward when composed together.
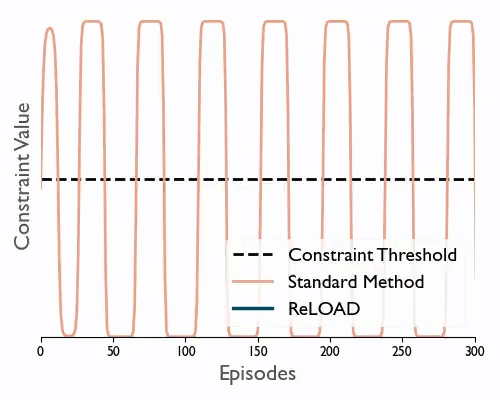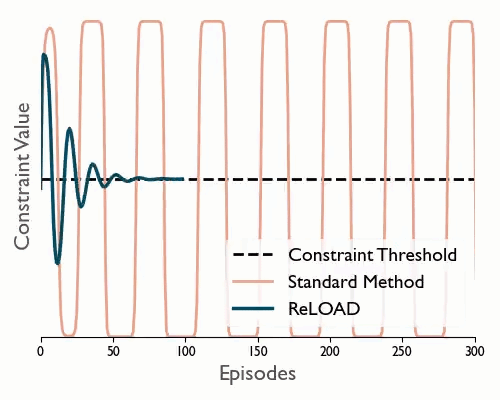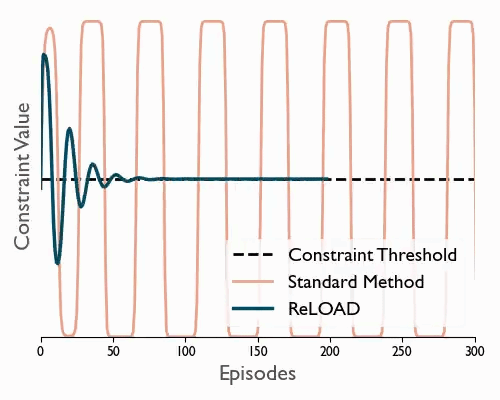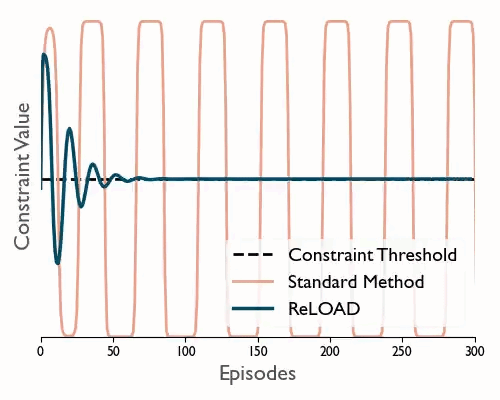
ReLOAD: Reinforcement Learning with Optimistic Ascent-Descent for Last-Iterate Convergence in Constrained MDPs
Tl;dr We propose a practical DRL algoritthm that converges (last iterate) in constrained MDPs and show empirically that it reduces oscilations in the DM control suite.
Ted Moskovitz, Brendan O'Donoghue, Vivek Veeriah, Sebastian Flennerhag, Satinder Singh, Tom Zahavy
Discovering Diverse Nearly Optimal Policies with Successor Features
Tl;dr We propose a method for discovering policies that are diverse in the space of Successor Features, while assuring that they are near optimal using a constrained MDP.
Tom Zahavy, Brendan O'Donoghue, Andre Barreto, Volodymyr Mnih, Sebastian Flennerhag, Satinder Singh
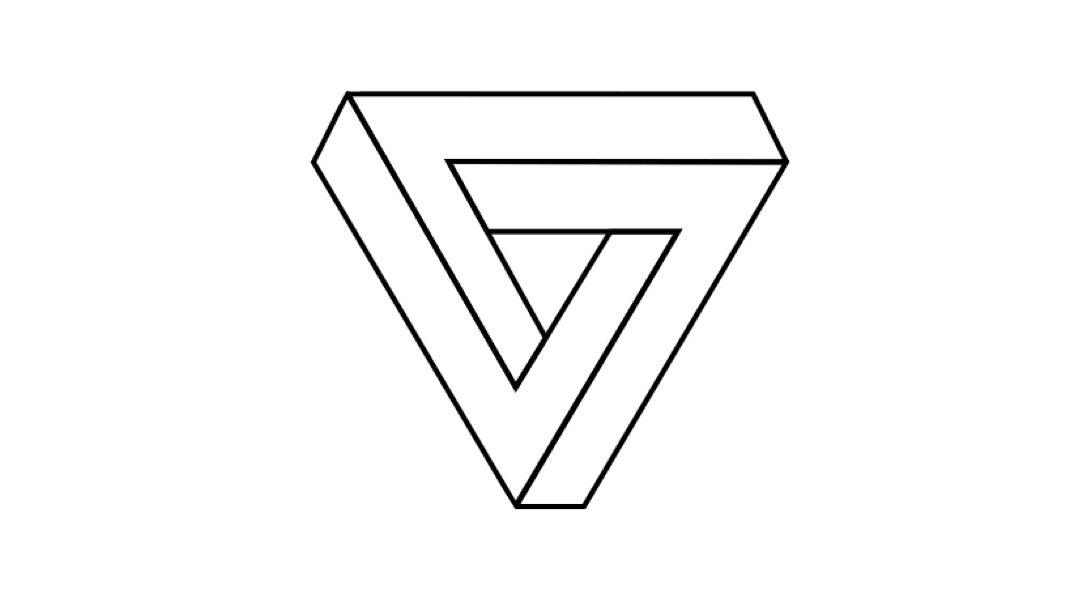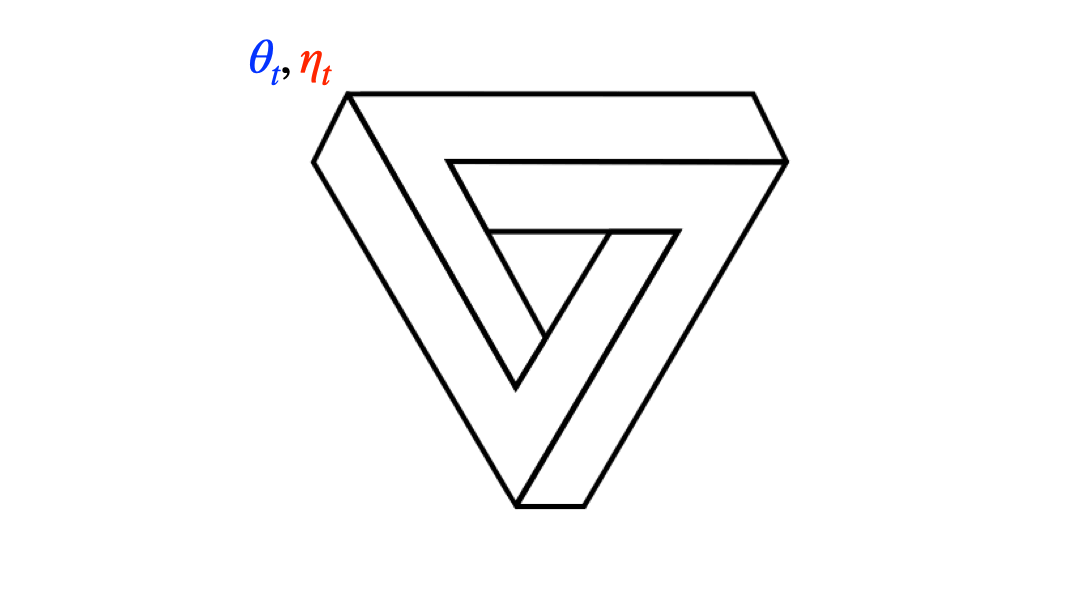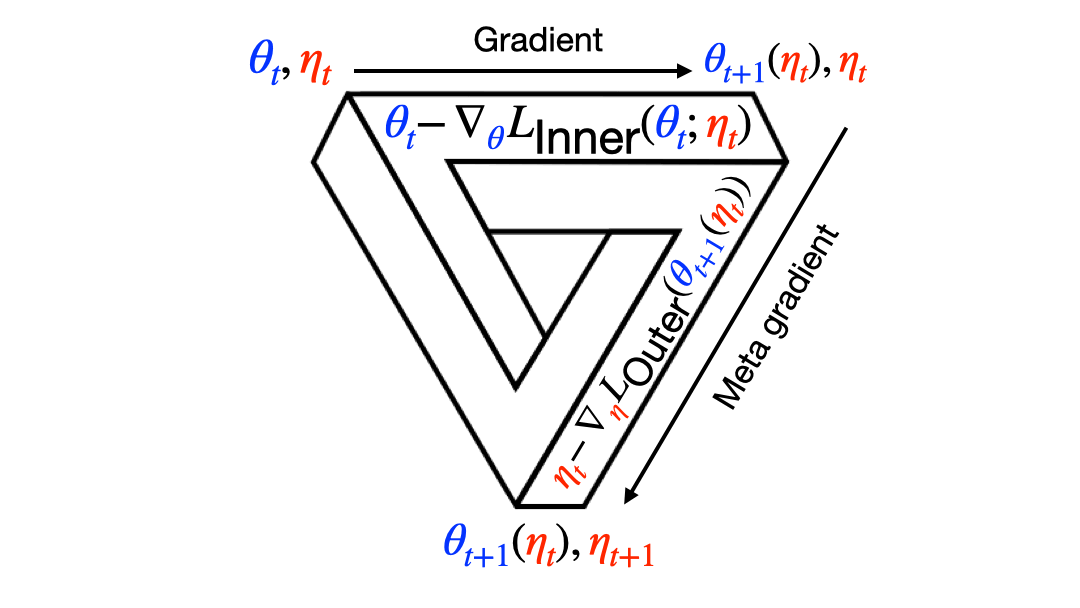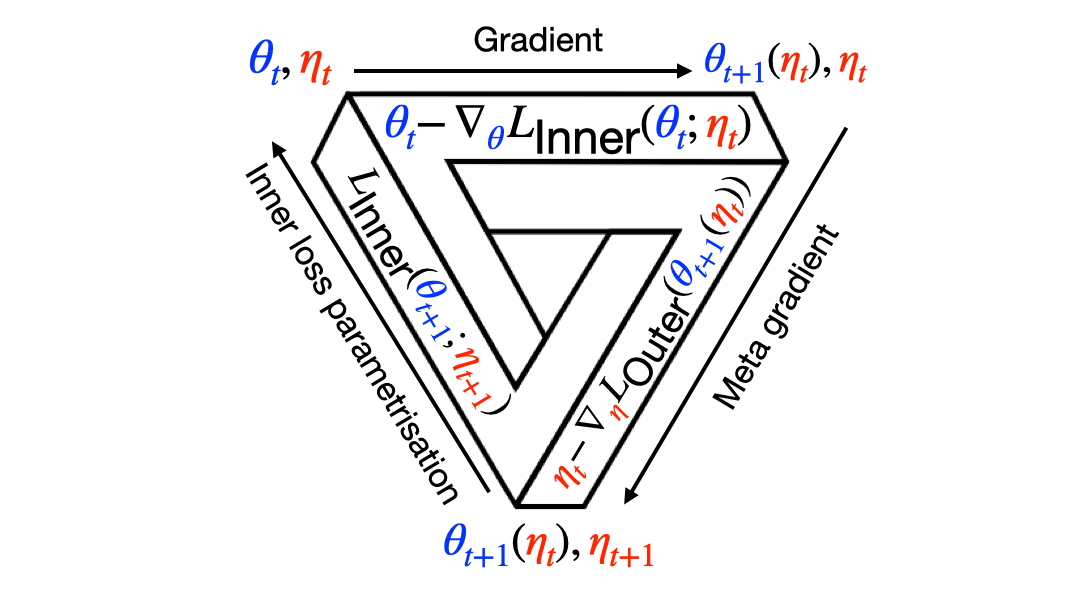
Meta RL: Building algorithms that learn how to learn and get better at doing so over time. I've worked mostly on meta-gradients, ie, using gradients to learn the meta parameters (hyper parameters, loss function, options, reward) of RL agents, so they become better and better at solving the original problem.
Read more about meta-gradients in my papers below, and please check out my interview with Robert, Tim, and Yanick in the MLST Podcast. I also recommend this excellent blog post by Robert Lange, and this talk by David Silver, featuring many meta-gradient papers including my own.
A Self-Tuning Actor-Critic Algorithm, NeurIPS 2020
Tl;dr: We propose a self-tuning actor-critic algorithm (STACX) that adapts all the differentiable hyper parameters of IMPALA including those of auxiliary tasks and achieves impressive gains in performance in Atari and DM control.
Tom Zahavy, Zhongwen Xu, Vivek Veeriah, Matteo Hessel, Junhyuk Oh, Hado van Hasselt, David Silver, Satinder Singh
Bootstrapped Meta Learning, ICLR 2022 (outstanding paper award)
Tl;dr: We propose a novel meta learning algorithm that first bootstraps a target from the meta-learner, then optimises the meta-learner by minimising the distance to that target. When applied to STACX it achieves SOTA results in Atari.
Sebastian Flennerhag, Yannick Schroecker, Tom Zahavy, Hado van Hasselt, David Silver, Satinder Singh
Discovery of Options via Meta-Learned Subgoals, NeurIPS 2021
Tl;dr: we use meta gradients to discover subgoals, in the form of intrinsic rewards, uses these subgoals to learn options, and control these options with an HRL policy.
Vivek Veeriah, Tom Zahavy, Matteo Hessel, Zhongwen Xu, Junhyuk Oh, Iurii Kemaev, Hado van Hasselt, David Silver, Satinder Singh
Balancing Constraints and Rewards with Meta-Gradient D4PG, ICLR 2021
Tl;dr: We use meta gradients to adapt the learning rates of the RL agent and the Lagrange multiplier in a constrained MDP.
Meta Gradients in Non Stationary Environments, CoLLAs 2022 (Oral)
Tl;dr: We study meta gradients in non stationary RL environments.
Jelena Luketina, Sebastian Flennerhag, Yannick Schroecker, David Abel, Tom Zahavy Satinder Singh
Discovering Attention-Based Genetic Algorithms via Meta-Black-Box Optimization,
GECCO 2023 (nominated for best paper award)
Tl;dr: We use evolutionary strategies to meta learn how to learn with genetic algorithms.
Robert Tjarko Lange, Tom Schaul, Yutian Chen, Chris Lu, Tom Zahavy, Valentin Dallibard, Sebastian Flennerhag
PhD papers
Graying the black box: Understanding DQNs
ICML 2016, featured in the New Scientist
Tom Zahavy, Nir Ben Zrihem, Shie Mannor
Online Limited Memory Neural-Linear Bandits with Likelihood Matching
ICML 2021
Shallow Updates for Deep Reinforcement Learning
NeurIPS 2017